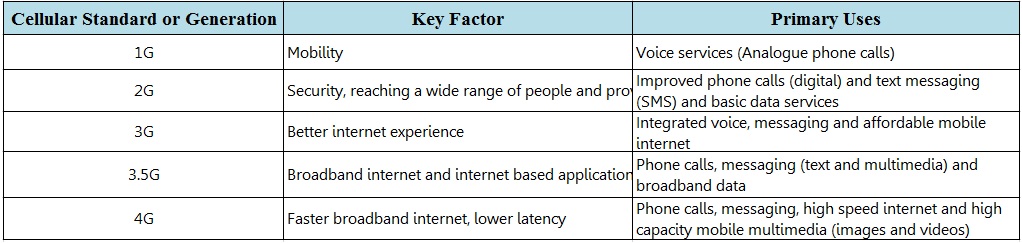
Right from that point of time, the concept of communication using a telephone has evolved into first long distance telephone call (at a distance of 6 miles) in 1876, Motorola’s first handheld mobile phone or cell phone in 1973, 1G or first generation analogue cellular network in 1979 in Japan, 2G or the second generation digital cellular network based on GSM technology in 1991, 3G or the third generation mobile communication based on UMTS and CDMA technologies in 2001 and the currently used 4G or fourth generation mobile communication technology based on LTE standard in 2009. With the developments in technology, the use of mobile phones is not restricted to just making phone calls. Several services like music, videos, camera, internet and internet based applications are integrated with the mobile phone. With the increase in the usage of the mobile phones and the requirement of higher bandwidths of internet, the next generation mobile communication technology, which is termed as 5G or fifth generation telecommunication technology, will be available in the distant future (2020 according to International Telecommunication Union – Radio communication sector’s International Mobile Telecommunication- IMT 2020 programme) and provides very high speed data rates. We cannot imagine the world without mobile phones and/or other hand held gadgets like tablets, smartphones, phablets etc. In fact, according to a survey, there are more number of mobile phones than the population of the world (the population of the world is 7.3 billion and the number of mobile phones is 7.5 billion). We can see millions of people with their hands on mobile phones making phone calls, texting, accessing the internet, getting the latest news, weather or sports updates, catching up with friends or family on social media like face book or twitter and watching online videos. We use mobile network to do the above mentioned tasks.
The fastest mobile network in the current market is 4G LTE standard or simply called as 4G network and can offer speeds up to 150 Megabits per second (150 Mbps when using an LTE Advanced network) for mobile users. With the increasing mobile connections and the continuous rise in the requirement of more mobile broadband, the future of mobile communication will be very different to what we are using today. With the growing impact of technology like ultra-high definition videos and high resolution screens in mobile devices, we will be even more “connected”. 5G is the next generation of mobile communication which offers huge bandwidths for data transmission, extremely robust system and ultra-low connectivity latency. According to technology experts, the transition from 4G to 5G will not be just an upgrade in the data speed, which was the case in transition from 3G to 4G, where the primary aim was to provide faster data speeds. Apart from providing ridiculously faster mobile broadband, 5G provides a network that is smart enough to understand the situation around the connected device. Internet of Things, a network where different appliances, systems and machines are connected in a network and communicate without human interaction with the help of several sensors. Even though 4G technology is said to be the key standard in internet of things (IoT), the challenges of providing a low latency network that consumes less power and operates at higher frequencies (lower wavelengths) for a wide machine to machine network were not provided by the 4G technology. With 5G coming in the distant future, the concept of wide Internet of Thing is not just a theoretical topic but can be implemented practically. With the help of 5G technology, the way we interact with the devices like mobiles, appliances and even cars will be completely different.
What is 5G?
5G is the next generation mobile communication technology which provides large bi-directional bandwidths. The data speeds in 5G can reach up to 10 Giga bits per second (10 Gbps). The effect of 5G will be on almost every industry like information technology, agriculture, automobiles, manufacturing, health, entertainment etc. Before defining the views on 5G, let us briefly understand the evolution of mobile technologies. History says that the evolution of each of the mobile communication technology or cellular standard is based on the key uses.
The key uses of 5G technology will not be the basic communication like phone calls or text messages. The key use of 5G will be in Internet of Things (IoT). Internet of Things or IoT is the communication between a large number of devices (machines or appliances) which continuously sense, process and transmit the data without any human involvement. An effective Internet of Things will require a reliable network with low latency, faster data rates, huge bandwidths and low power consumption.In theory, there are two views of 5G technology. They are the Hyper Connected Vision and the Next Generation Radio Access Technology. In the hyper connected vision view of 5G technology, the architecture of the 5G is a blend of previous technologies like high quality voice and SMS from 2G, voice, video and data from 3G, massive mobile data from 4G, best effort data from Wi-Fi, short range and low power from PAN (Personal Area Network) and other technologies to provide better connectivity, coverage and network density with the key use being the Internet of Things (IoT) and machine to machine communication. The next generation radio access technology is a more traditional view of the term “generation evolution” as its criteria being data rates and latency. Both these views are important in the development of the 5G technology. Even though they have different sets of requirements, the hyper connected vision and the next generation radio access technology view are clubbed together and taken as a single set. Hence, the potential architecture of the 5G technology can be considered as a combination of existing systems like 2G, 3G, 4G, Wi-Fi, PAN and evolving systems like software defined network (SDN), next generation wide area network, extremely low latency and GB data transfers. All these technologies are integrated and harmonized so that they are complementing each other.
5G Technology Specifications
The parameters and their standards are yet to be defined for 5G technology. But from the estimated requirements of the 5G technology, some of the specifications can be defined as follows:
Data Rates: 1 to 10 Giga bits per second (Gbps) to the end mobile users. Latency: Less than 1 millisecond (< 1ms). Bandwidth: 1000 times the present bandwidth per unit area. No. of devices: 10 to 100 times the current number of devices. Network Coverage: 100% Signal Availability: 99.999% Power Consumption: 90% reduction in energy usage.
5G Challenges
The development of a new communication technology is dependent on many factors like economies of different regions, globally accepted standards, cost, supporting infrastructure, availability to end user etc. The following are some of the many challenges that the 5G network is expected to achieve at operational level:
1000 times wider area coverage of the wireless network that it is in 2010. The ratio of Power consumption to service provided, particularly in mobile devices is expected to fall by 90%. Providing a reliable network to connect over 7 Trillion devices in the Internet of Things that are controlled by over 7.5 Billion people. Allowing advanced end user controlled privacy. Providing a faster, secure, reliable and robust network with theoretically zero (practically very small or close to zero) downtime.
The above mentioned challenges are more technology oriented and relate the development of the new communication technology to the evolution of the mobile communication. There are two other challenges that are more general and physical in nature. They are standardization and infrastructure. The standardization of the 5G technology is the main challenge with the IMT 2020 vision. Several standardization bodies are working towards the 5G definitions and the base technical specifications are set to be rolled out in 2016. The more physical challenge is setting up the infrastructure supporting the 5G technology. This includes allocating the spectrum and installing new antennas related to that spectrum range.
Research and Studies in 5G Technology
The estimated commercial launch of 5G is expected in 2020. Hence, many institutions, technological companies and research organizations are collaborating to form committees towards the research into 5G Technology. Some of the key areas of research are mentioned below:
Centimeter and Millimeter Wave
There is a significant amount of spectrum available at higher frequencies. 5G technology is looking beyond the congested centimeter waves which have the frequency range of several hundreds of Megahertz and are occupied by the current 3G and 4G networks. The advantage of using millimeter waves for mobile communication is wide channel bandwidth of 1 to 2 Gigahertz in contrast to the current bandwidths of 10 to 20 Megahertz. There are many challenges in going to millimeter wave technology, which have the frequency range of 3 to 300 Gigahertz, like circuit level design of devices like mobiles, range of the signal and penetration of the waves.
Massive Dense Networks or Massive MIMO
Massive MIMO or Multiple input and multiple output helps in reaching the goals of next generation telecommunication system to provide higher data rates to more users. It is being used in existing technologies like LTE (4G) and Wi-Fi, but the number of antennas are restricted. With the use of millimeter waves in 5G communication, massive MIMO can use a very large number of antennas (theoretically infinity).
Battery life
Batteries that can last years are very important in Internet of Things network as the machine connected to the network may not be near a power source. 5G technology can be characterized for more efficient use of power for extended battery life.
Cognitive or Smart Radio Technology
It is a dynamically programmable radio system where the transmission and reception of signals is designed to use the best available channel in the proximity.
Pervasive or Ubiquitous network
This allows the user to be connected to different wireless technologies like 2G, 3G, 4G, Wi-Fi, etc. at the same time and can switch between them without any hassle.
Potential uses of 5G
5G technology has a potential use in many industries like education, medicine or health, information technology, entertainment, automobiles, manufacturing etc. Some of the potential uses of 5G technology are mentioned below.
Virtual Reality or Tactile Internet
An example of this technology is the remote controlled surgery robot where high bandwidth and low latency are required. Such systems are still in early stages of development and are highly dependent on other systems like motion sensors and displays.
Autonomous Cars
Autonomous driving or smart cars and connected cars are automobiles which can communicate with outside world or other cars so that road journey will be safer even with the current infrastructure.
Internet of Things
The concept where a number of devices – machines, appliances or systems are connected to each other and sense, process and transfer data among them without any human control. Such systems require a reliable, high bandwidth and low latency network and can be possible by 5G.
Machine to Machine connectivity
The best example of machine to machine communication is in a smart home automation system where different devices like meters, temperature control, security, smoke detection etc. are connected to and communicate with each other and work efficiently. Some of the other machine to machine communication systems are deployed in consumer electronics, automobile telemetry, automated health monitoring etc. Most of these connections are still using either 2G or 3G networks. There might not be an immediate transition to 5G technology but eventually all machine to machine connections make use of 5G technology.
Wireless Cloud Computing
The concept of wireless cloud office where huge amounts of data can be stored and accessed remotely. This is possible with high bandwidth communication systems. The present 4G network has the potential to deliver this service as they do not require low latency.
Multi person Video Calling
Another service where bandwidth and latency are important is multiple video conference. Even though this requires low latency, the existing 4G technology can handle the data.
Does this mean the end of 4G?
The answer is no. Less than half of the mobile markets have 4G LTE technology. Even though 4G LTE is spreading faster than 3G was, it will take almost a decade for 4G to achieve more than 90% penetration worldwide. 4G LTE is still in its early stages of expansion and with new 4G standards like LTE Advanced coming to the mobile market, there will be no immediate threat to 4G even after introduction of 5G (estimated arrival is in 2020). Mobile network operators continue to invest in 4G and expect a return for another two decades by increasing data speeds, reducing the price over the years etc. Image Contributors 1)Mobile Phones static.guim.co.uk 2)5G Image cdn1.itpro.co.uk 3)1G to 4G Evolution europa.eu 4)5G Challenges orange.com 5)5G Research ericsson.com 6)5G Uses ericsson.com Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ






![]()