If you are aware of motherboards you may have also heard the terms ATX and BTX. They are a form factor of motherboards and play a very crucial role in improving the PC’s performance and versatility. In this article, we will discuss the Advanced Technology eXtended (ATX) and Balanced Technology eXtended (BTX) to help you learn basic differences between them and see which form factor is better. So, without much further ado, let’s start.
What is ATX?
Advance Technology eXtended or ATX is the most common form factor of a motherboard in the computer world. But this was not the case until 1995. Before ATX became a standard form factor, motherboards used to come with Advanced Technology (AT) design. However, AT motherboards lack capabilities and needed replacements. This is where Intel grabbed the opportunity and introduced ATX which became a successor of AT in terms of speed, interface, and performance. The introduction of ATX is considered one of the biggest changes in power supply design, motherboard, and computer enclosure as it improved standardization and interchangeability of parts. A full-size ATX board is 12 x 9.6 inch which is considered a standard form factor. A Micro-ATX or mATX is 9.6 x 9.6 inches making it a perfect option for budget-friendly gaming PCs, but the availability of PCle slots can be an issue. Then comes an EATX motherboard variant which supports dual-socket and larger surface area dissipate heat better.
Pros and Cons of ATX
Here below are some pros and cons of the ATX motherboard that you must know. Pros: 1: Expansion – the sufficient size of the ATX form factor allow enough slots and ports for expansion. 2: Upgrades – because there are lots of ports and slots in this motherboard, there will be no hindrance when and if you upgrade your system. 3: Interchangeable parts – the ample size of the ATX motherboard allow you to remove or add parts to your motherboard. Cons: 1: Blocks airflow – the arrangement and position of components placed in an ATX board can disturb the airflow which could result in less cooling. 2: Price – another disadvantage of this form factor is the high price. However, you can choose the mATX variant by compromising aesthetics, and RGB LEDs.
What is BTX?
ATX VS EATX Motherboard ATX vs Micro ATX vs Mini ITX – Which One Should You Choose? Best Micro ATX Motherboards
BTX or Balanced Technology eXtended is a form factor of the motherboard that was introduced by Intel in 2004. It was designed to replace the de facto standard – ATX. Balanced Technology eXtended was introduced to solve major problems that existed in the ATX form factor. The biggest problem that existed was ‘heat’. The ATX’s component arrangement hindered airflow that resulted in less cooling. When BTX came, the location and design of the components (processor chip, northbridge chip) was altered which made this form factor better than the ATX board in terms of cooling. This became the biggest advantage of BTX over ATX. However, despite being better than ATX in terms of cooling, people do not prefer this form factor because of the following reasons:
People already invested in ATX systems and don’t want to change. BTX is more expensive in comparison to ATX. Most users simply do not care about the cooling factor.
There may be other reasons why people choose ATX rather than BTX. One biggest and obvious reason is that Intel has discontinued the development of the BTX board.
Pros and Cons of BTX
Let us now see what advantages and disadvantages a BTX form factor carries. Pros: 1: Better airflow – the biggest advantage of the BTX board is that it focuses on airflow and delivers better cooling than ATX. 2: Reduced latency – the design, new component location on the board reduces latency. 3: Stability – Efficient cooling provided by this form factor offers component durability as well as system stability. Cons: 1: Price – Though BTX offers utilities, it costs more than ATX. 2: No upgrade – Intel has stopped developing this technology. Instead, they focus on reducing the power of the CPU, hence reducing heat and making ATX effective.
Comparison Table between ATX and BTX
To help you grasp the information better, we suggest you have a quick glance at ATX and BTX comparison table.
Main Differences between ATX and BTX
In debates, the most common difference between ATX and BTX is regarding the board design and cooling performance which is correct, but here is our answer to this subject:
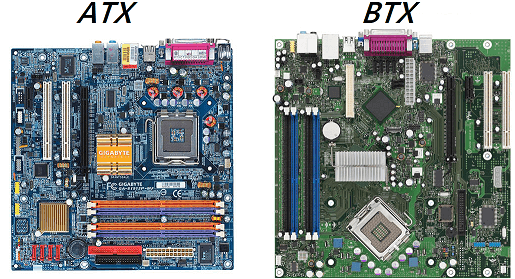
ATX is the successor of AT design and is currently the de facto standard of the motherboard. BTX was initially introduced to replace ATX but couldn’t succeed in doing so. ATX board design and component placement resulted in less airflow and more heat, so BTX was invented to solve this problem. The Balanced Technology eXtended altered the location of the components and created a technology with better airflow and effective cooling. In an ATX motherboard, you will find IO ports on top of the board, whereas in BTX it is situated below the board. BTX board requires special arrangements to maximize the cooling, but in the ATX board, no such arrangement is required. BTX system development is discontinued by Intel, which means it is rarely found in PCs. ATX, which is currently dominating the market is upgradable and is common in PCs.
Conclusion
ATX and BTX are form factors of the motherboard. Balanced Technology eXtended is the advanced version of Advanced Technology eXtended and was introduced to replace it in 2004, nearly after ten years when ATX was invented. In the BTX board, essential components like the IO ports, slots, memory modules, etc. are situated below the board to maximize the airflow. This makes BTX better than ATX in terms of cooling. However, only one quality could not simply become the dominating force of the market. Despite providing effective cooling, BTX was and is not preferred by people. In contrast, people prefer the ATX system due to its performance, speed, expansion capabilities, upgrades, etc. and this is why ATX is widely used in PCs in comparison to BTX. Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ






![]()