These relays provide a “Time Delay” between the energizing or de-energizing of the coil and movement of the armature. Such relays are called Time Delay Relays. A Time Delay Relay consists of a normal electromechanical relay along with a control circuit to control the relay operation and timing.
The main difference between a regular relay and a time delay relay is that in case of a normal relay, the contacts are close or open immediately when the coil is energized or de-energized while in case of time delay relay, the contacts are close or open only after the preset time interval. In this project, a simple 12V Time Delay Relay is designed using a regular electromechanical relay and some additional circuit to provide the timing function. [Read:Adjustable Timer Circuit]
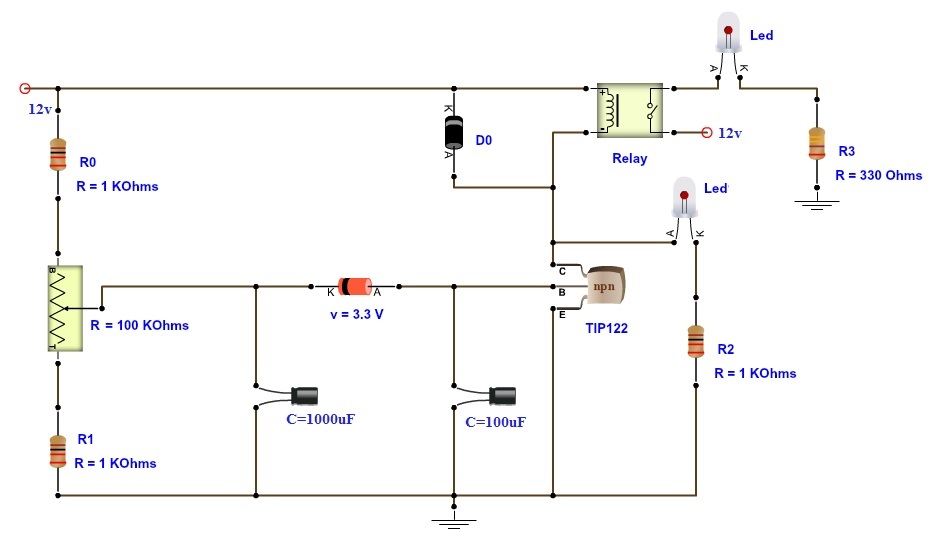
Circuit Diagram
Components Required
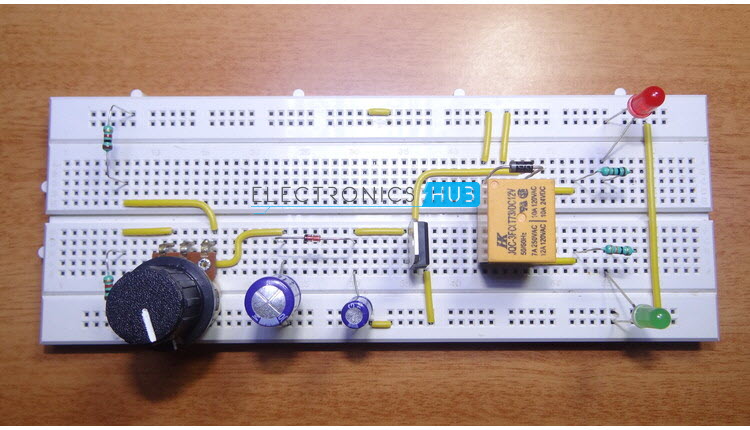
12V Relay — 1 TIP122 — 1 1N4728A (3.3V Zener) — 1 100 KΩ POT — 1 1KΩ — 3 330Ω — 1 1000µF / 25V — 1 100µF / 25V — 1 1N4007 — 1 LEDs — 2
Circuit Design of Time Delay Relay
A 1KΩ resistor, a 100KΩ variable resistor and another 1KΩ resistor are connected in series between the supply and ground. The wiper of the variable resistor is connected to the positive terminal of a 1000µF capacitor. The wiper terminal of the variable resistor is also connected to the cathode of the Zener diode. Anode of the Zener diode is connected to positive terminal of 100µF capacitor. Anode of Zener diode is also connected to the base of transistor TIP122. Negative terminals of both the capacitors and the Emitter terminal of the transistor are connected to ground. One end of the relay coil is connected to the Collector terminal of the transistor and the other end of the coil is connected to supply. A diode is placed between the coil terminals. An LED along with a current limiting resistor is connected from the collector of the transistor. To show the switching operation of the relay, an LED is connected to Normally Open contact of the relay and the Com contact is connected to supply.
Working of Time Delay Relay
Modern day electronic devices use SMPS based power supply systems. Such power systems are vulnerable to spikes in mains power supply. Input surge current at power on or power resuming after failure can cause severe damage to SMPS systems in electronic devices. Hence, it is safe to provide a time delay before giving the power to device. This prevents the disastrous effects of voltage spikes or input surge currents. The aim of this project is to demonstrate the functioning of a time delay relay. Time Delay Relay can provide a short delay after power is turned on and before switching on the device. The working is very simple and is explained below. The circuit is based on the RC time delay and Zener controlled switch. When the power to the circuit is turned on, the 1000µF capacitor charges through the 100KΩ variable resistor. Once the charge across the 1000µF capacitor reaches 3.3V, Zener diode starts conducting. As the Zener is connected to the base of the transistor, it triggers the transistor and it is turned on. The relay coil is connected to collector of the transistor. Hence, the relay coil gets energized when the transistor is switched on. As a result, the contacts of the relay switch. The 100µF capacitor that is connected to the base of the transistor, is used to keep a stable base bias of the transistor so that there are no relay clicking. The delay of the relay can be controlled by variable resistor and 1000µF capacitor. For shorter delays, the circuit works fine but for longer delays, a 12V relay may be unstable and oscillations of the armature can be found. For longer delays, it is advised to use a 6V relay with a 100Ω resistor in series with the coil must be used. This will stabilize the armature operation even for longer delays. When the variable resistor is kept at 20KΩ, the delay is about 8 seconds. NOTE
A simple time delay relay circuit is designed here. With the help of this circuit, a user controlled delay to relay can be given. Time delay relays are very useful in protecting sensitive electronic devices from spikes and surges.
Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ





![]()